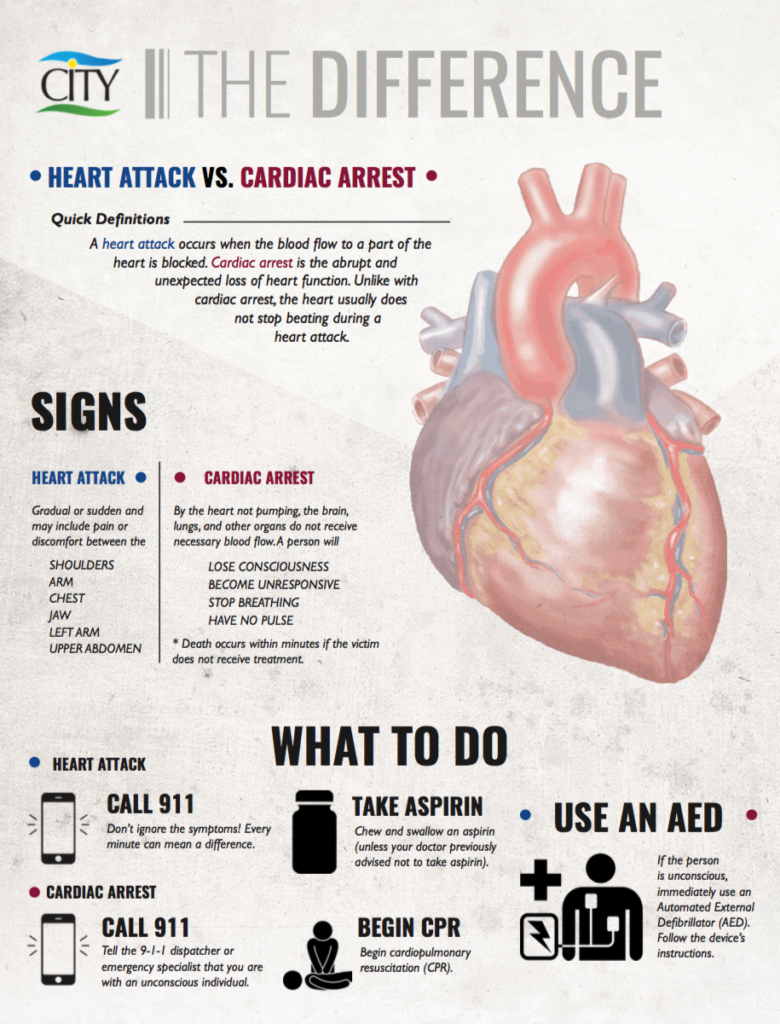
Know the Difference: Heart Attack vs. Cardiac Arrest
Do you know the difference between a heart attack and sudden cardiac arrest? Many people use these terms interchangeably, but they have very different meanings.
What is a heart attack?
A heart attack occurs when the blood flow to a part of the heart is blocked. This prevents oxygen-rich blood from reaching a section of the heart. Unlike with cardiac arrest, the heart usually does not stop beating during an attack.
The Signs
Symptoms of a heart attack may be sudden and may include pain or discomfort between the shoulder blades, arm, chest, and jaw, left arm or upper abdomen. Other symptoms include shortness of breath, dizziness, nausea, lightheadedness, and sweating. Symptoms also vary among men and women.
The longer the person goes without treatment, the greater the damage.
What to Do
- Call 9-1-1. Don’t ignore the symptoms! Every minute you wait can mean a world of difference.
- Chew and swallow an aspirin (unless you are allergic or have been told by your doctor never to take aspirin).
- Begin CPR is the person is unconscious. Tell the 9-1-1 dispatcher or another emergency medical specialist that you are with someone who is unconscious. You may be advised to begin cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR).
- Use an automated external defibrillator (AED) if it’s immediately available and the person is unconscious. Follow the device’s instructions.
What is cardiac arrest?
Cardiac arrest is the abrupt and unexpected loss of heart function in a person who may or may not have diagnosed heart disease. The condition occurs instantly or shortly after symptoms appear.
The Signs
By not pumping, the brain, lungs, and other organs do not receive necessary blood flow. A person will lose consciousness/responsiveness, stop breathing, and have no pulse. Death occurs within minutes if the victim does not receive treatment.
What to Do
- Call 9-1-1.
- Start CPR immediately. Tell the 9-1-1 dispatcher or another emergency medical specialist that you are with someone who is unconscious. You may be advised to begin cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR).
- Use an automated external defibrillator (AED) as soon as possible. Follow the device’s instructions. If a victim receives defibrillation within the first minute of collapse, the victim’s chances for survival are close to 90%.
The Connection
Many cardiac arrests occur in adults because of a heart attack. This is because a person who is having a heart attack may develop a dangerous heart rhythm, which can cause cardiac arrest.
To learn more about how CITY can help your business with CPR training and AED devices, go to www.CITYSafeAndSimple.com/.
Comments
Comments are closed.